Quick Take
Oracle solves the problem of transferring data from off-chain to on-chain, while essentially, transferring data is not difficult, the most important thing is to solve the problem of data trust, thus decentralized oracle can avoid creating a single point of failure of the centralized propagator, but accordingly, the decentralized propagator is more expensive to use due to the need to pay for services to multiple nodes.
As the earliest group of Chainlink data providers, Wetez is very happy to witness the growth of Chainlink who now is the world’s largest oracle network. Oracle data provides important data for what are known as decentralised financial applications (DeFi) and other industries, through which transactions worth several billion US dollars are now processed daily, such as on Aave and Uniswap. Being as the oracles‘ data provider, Wetez is expanding its expertise in the crypto infra and continue providing high-quality, state-of-the-art technology services as a trusted supplier.
What is oracle?
The word oracle originated from the role of "oracle" in ancient Greek mythology. According to legend, the oracle could communicate with the gods on Mount Olympus, make predictions about the future, and convey the gods' will to the people who prayed for the future, so oracle first had the meaning of "prophet". In the theory of computational complexity and computability, an oracle machine is an abstract computer used to study deterministic problems and can be regarded as a Turing machine with a black box (prophet) attached.
We know that blockchain is a consensus-based network, and the inherent limitations of its consensus mechanism and its deterministic virtual machine stipulate that smart contracts can only passively receive data. Neither can they actively access Internet data nor spontaneously call external network APIs, but most blockchain scenarios such as insurance and lending require active real-time access to data in the real world, especially the Internet.
Therefore, the oracle generally interacts with the execution engine as an independent module of the blockchain or as a third-party service. oracle is a tool for passing off-chain data to on-chain smart contracts and also for transferring on-chain data to the off-chain world.
It only responsible for the trusted acquisition of data and is not directly involved in the execution of transactions. Among the various oracle projects, most of them act as "middleware" between the physical world and the block world, allowing smart contracts to actively access external data. Without the oracle, the only data that a smart contract can use is the data generated on-chain, and it cannot use the external data.
How is Crypto oracle market?
As mentioned before, oracle solves the problem of transferring data from off-chain to on-chain, while essentially, transferring data is not difficult, the most important thing is to solve the problem of data trust, how to make the data passed to the chain really trustworthy and reliable is the real problem to be solved by the oracle.
Depending on the design of the trust mechanism, there are three kinds of oracles:
- Centralized oracle
- Affiliate oracle
- Decentralized oracle
Centralized oracle
Centralized oracle uses single data source, usually with data provided by a trusted third party such as a government or a reputable company. It prevents data tampering and loss by separating the data from the local device's untrusted operating system. However, a single centralized data source also poses a potential risk to smart contracts.
Since there is no need for the multiple nodes to cooperate, it saves a lot of time and improves efficiency of the oracle, and because multiple nodes are not needed to support the service, there is no need to pay for a multi-node network and the usage cost is relatively lower.
While the disadvantages of centralized oracle is the single source of data and limited data volume, since centralized oracle is based on the user's trust in the institution. A single data source cannot avoid a single point of failure, and there is no restraint on evil-doing, and security is difficult to guarantee.
Affiliate oracle
Affiliate oracle is a special form of decentralized oracle. The network of nodes is composed of not only normal nodes but also some designated trusted institutions as nodes. For example, the v2 version of MakerDAO's oracle has nodes that include organizations such as dYdX and 0x.
The source of trust in the affiliate oracle is more complex than the previous two, including trust in the reputable organizations as nodes and the whole network, as well as the node selection mechanism of the affiliate oracle project. Data users need to trust that all these interested parties will not choose to act in a way that harms their own reputation for profit.
The composition of this node network is somewhat centralized, but as a cost-effective trade-off, it is not a bad choice in the early stage of industry development. It is just that this kind of trust mechanism with centralized coloring may be difficult to carry the demand of smart contracts with too much value.
Decentralized oracle
A decentralized oracle has distributed consensus mechanism, also known as a consensus Oracle. It obtains data from multiple rather than single external sources, so it is more reliable and does not require trust.
Because multiple nodes need to work together, the size of the node network of a decentralized prophecy machine affects the reliability of the data it provides, and the data provided by a larger network has higher reliability, so the system usually provides some economic incentives to encourage more nodes to participate.
Nodes involved in providing services are also usually required to pledge a portion of their tokens (usually the project tokens themselves) when providing data, and the pledged tokens will be confiscated once the system finds that the node has committed evil acts.
The decentralized node network can avoid creating a single point of failure of the centralized propagator, but accordingly, the decentralized propagator is more expensive to use due to the need to pay for services to multiple nodes.
How decentralized oracle works?
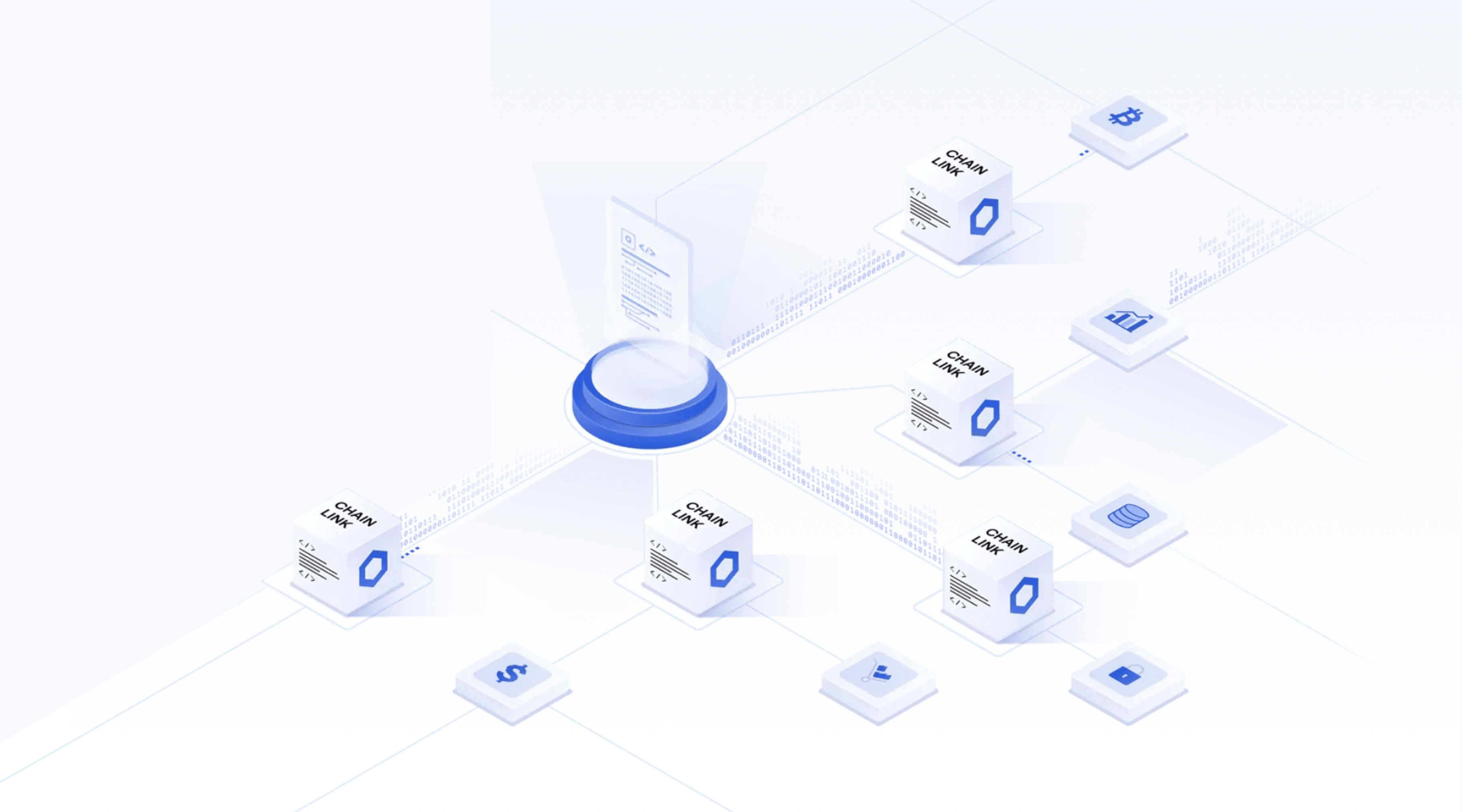
We use Chainlink as an example. It provides data for smart contracts through on-chain reputation contracts, node-matching contracts, aggregation contracts and decentralized off-chain oracle network. Chainlink is the first decentralized oracle project, founded in December 2014. On May 30, 2019, Chainlink was officially launched on the main Ethereum network, with a first-mover advantage and positive network effects, becomes the the most widely used Oracle.
Chianlink have multiple independent oracle data providers and a plenty of data sources to increase the decentralization of its network. In addition, in order to guarantee the quality of data and prevent the oracle data providers from doing evil, Chainlink has designed a reputation system and a staking mechanism to rate the performance of chainlink data providers, reward the nodes with LINK for good performance, and deduct the LINK staked by nodes with misbehavior.
Generally speaking, the workflow of Chainlink can be divided into two parts: on-chain and off-chain. The on-chain module is responsible for connecting the smart contracts of DApp developers and accepting requests for data, while the off-chain module is responsible for listening to requests and obtaining data from data providers.
The on-chain part of Chainlink consists of three modules, namely, reputation contract, order matching contract and aggregation contract, which are responsible for selecting oracles, reporting data and aggregating data. The lower part of the chain is a network of independent oracle data providers that listen to requests and obtain data from data providers.
What is decentralized oracle data provider?
Oracle node operators also known as the oracle data provider, they are the backbone of decentralized oracle Network. Oracle data provider are the entities running the oracle infrastructure (hardware and software) that powers and secures every oracle network running on the Network. These oracle data providers are responsible for watching the blockchain for new incoming data requests from smart contracts, fetching the requested off-chain data from specified APIs, and delivering the data on-chain where it can be consumed by a smart contract to trigger its execution. Similar to how the Internet connects computers to the outside world, oracles are the bridge between a blockchain and any piece of data or system that exists outside of it.
Wetez, as the earliest group of oracle data providers, has been as Chainlink data provider and its data provider network member since 2019. As a part of Chainlink DON network, Wetez offers over 140+ price feeds in three networks. In order to guarantee the neutrality and reliability of data source, Wetez accesses the API interfaces of multiple premium paid data aggregators, such as embedding certificate management capabilities to access password-protected API interfaces When the feed price needs to be updated, Wetez fetches data from multiple data aggregators and returns the median value. Wetez improves service reliability by automatically rejecting outliers and preventing data aggregators' APIs from going offline unexpectedly.
After aggregating data, Wetez together with other data providers form a network of DON (decentralized oracle network) that periodically generates oracle reports containing the data points uploaded by each data provider. Every report includes a great number of data points (median data feed) as well as signatures (cryptographic verification). The oracle reports generated by the DON are then stored in a reference smart contract for a specific dataset on the chain (e.g., the reference contract for BTC/USD on Ether). Each time a oracle report is published on the chain, the signature of each data provider is verified before the median is extracted for all data and stored in the reference contract, which cannot be tampered with once the data is stored.
To maintain a high level of tamper resistance, at least 2/3 of the data providers in a DON need to upload their results and signatures for the oracle report to be accepted on the chain. This prevents a data provider or a small group of data providers from manipulating the final feed price or publishing incomplete oracle reports on the chain. Also, since the oracle report takes the median when it is published, at least half of the oracle data providers must be bribed if the final results stored on the chain and entered into the smart contract are to be manipulated.
How's Wetez doing?
As the earliest group of Chainlink data providers, Wetez is pleased to witness the growth of Chainlink and it now become part of the world’s largest oracle network. By offering more than 140+ price feeds in two networks and serving as Chainlink data provider for 4 years, Wetez demonstrates its professional data processing and robust operating ability.
Being as the professional Web3 infrastructure provider since 2018, Wetez is the critical Web3 infrastructure that provides the tools that enable developers to easily access their blockchain from testing to scaling deployed applications. With 99.9% uptime, over $80 million staking assets for 50+ blockchain projects, over $24 million generated rewards, Wetez provides services that cover from Appchain construction, dApp building, node operation, to API, data storage, data analysis, etc. Wetez will continue to provide robust services and being as the reliable cornerstone for the growing popularity of Web3 and help unlock the next generation of blockchain use cases.